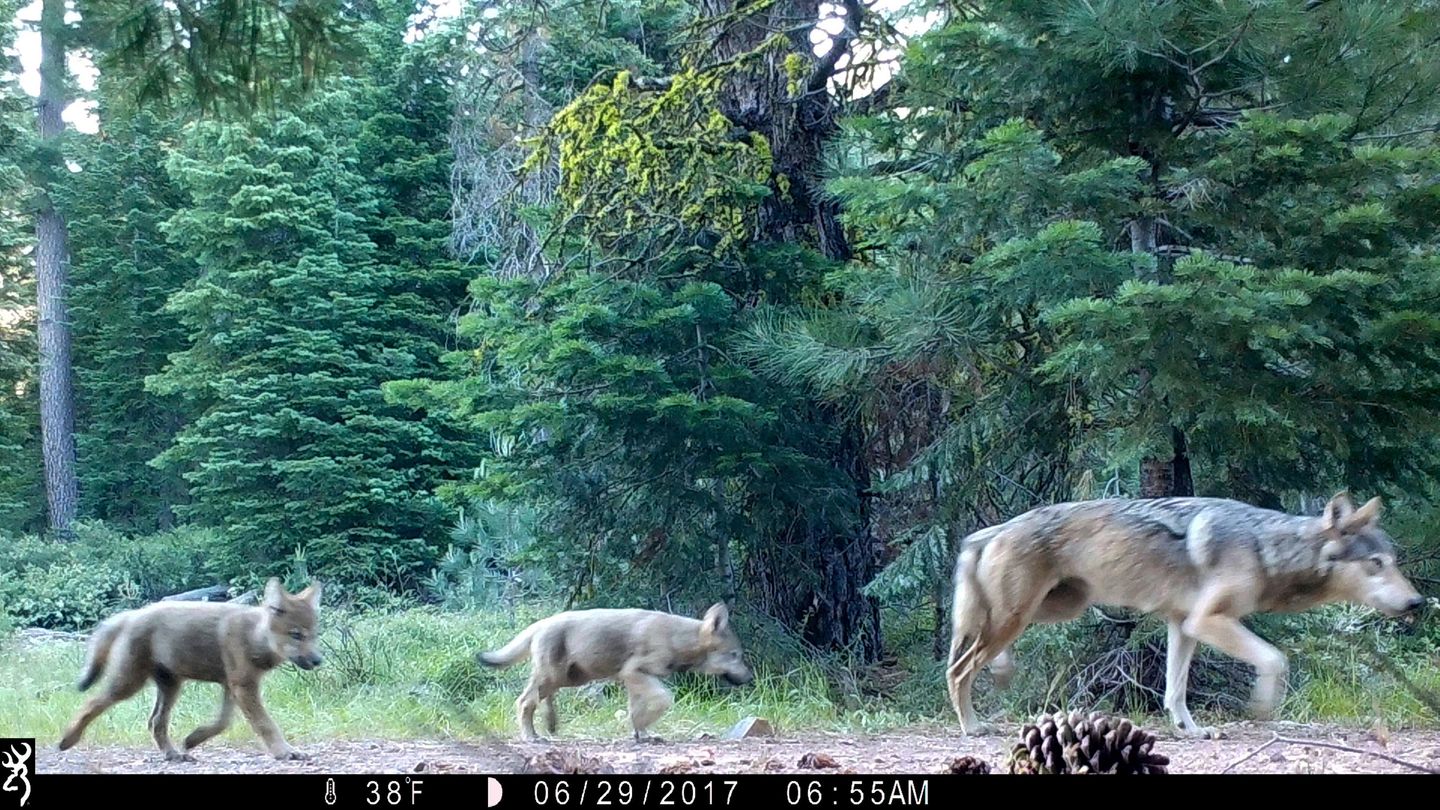
SAN FRANCISCO — Wildlife crews are no longer actively searching for two juvenile gray wolves who were part of a pack that killed dozens of cows and calves last summer in Northern California’s Sierra Valley, an official said Tuesday.
The two wolves were members of the Beyem Seyo pack that in 2025 killed or injured at least 92 calves and cows in a seven-month period, according to a report released last week by two researchers with the University of California, Davis.
Wolves in the state are protected under California law and the federal Endangered Species Act. Under former President Joe Biden, officials said they planned a first-ever national recovery plan for wolves, but President Donald Trump’s administration ended that initiative in November.
In October, the California Department of Fish and Wildlife announced it had euthanized four gray wolves – three adults and a juvenile – from the Beyem Seyo pack after “an unprecedented level of livestock attacks across the Sierra Valley.” It also said it planned to capture and relocate the remaining two wolves to wildlife facilities to prevent their behavior from spreading to other wolves in California.
Gray wolves primarily prey on wild animals like deer and elk, not livestock, the department said, calling the attacks by the Beyem Seyo against farm animals “unprecedented.”
“These wolves had become habituated to preying on cattle, a feeding pattern that persisted and was being taught to their offspring which would leave to form their own packs and could teach them the same cattle-preying behavior,” the department said at the time.
But following weeks of searching for the remaining two wolves, officials have “reduced efforts to capture” them, Katie Talbot, CDFW Deputy Director of Public Affairs, said in a statement.
“Despite best efforts from CDFW’s expert wolf biologists and law enforcement officers, we have not been able to find or get close enough to these young wolves to safely capture them,” Talbot said.
“We remain hopeful our continued remote monitoring will allow for sightings that will lead to safe capture of these juveniles,” she added.
Wildlife officials tried for months to deter the pack from attacking farm animals by using drones, nonlethal bean bags, installing flags or rope to deter them and having officers in the field 24 hours a day, seven days a week, but their efforts failed.
Gray wolves were eradicated in California early in the last century because of their perceived threat to livestock, with the last known native wolf killed in 1924 in Lassen County. Since their reintroduction in Idaho and at Yellowstone National Park in the mid-1990s, they’ve proliferated, with a pack reappearing in Northern California in 2015. The recovering population has meant increasing conflict with ranchers.
“It was a horrible summer here for everybody and the emotional strain was probably worse than the financial strain for most people. They did the right thing. We couldn’t go on living the way we were living,” said Rick Roberti, a cattle rancher in Plumas County and president of the California Cattlemen’s Association, who lost several animals.
Economist Tina Saitone and researcher Tracy Schohr said in UC Davis’ quarterly agricultural economics update released Friday that the Beyem Seyo’s pack depredations were unprecedented not only in the state but also nationally. The pack killed more livestock than the entire wolf population of Montana killed in 2024 and the killings of farm animals by the wolves in Wyoming in 2023.
In Montana, the state’s 1,100 wolves killed 54 domestic animals in 2024, and Wyoming’s 352 wolves killed 49 livestock in 2023, the scientists said.
In California, about 70 gray wolves were responsible for 175 livestock kills between January and October of last year, with the Beyem Seyo pack responsible for half of the killings, according to CDFW data.
Roberti said the attacks on livestock in Plumas and Sierra counties left many ranchers angry. He said he would like to see certain areas in the state declared “special zones” where people are allowed to hunt wolves that attack livestock.
“We’re pretty much in unison about thinking that it would help if we started taking out the ones that are just killing cattle and are too habituated to man or they’re not afraid of us,” he said.